Manual Using Colors of Fracthunder 2.1
Using the Pipet
The FracThunder has one pipet. On the toolbar you see a circle of a color, that is de content of the pipet.
Filling the Pipet
You can (re)fill the pipet with another color:
- Press
 or choose in the menu:Mode | Pipet.
or choose in the menu:Mode | Pipet.
The Cursor will change into a pipet.
- Click in a fractal.
The pipet will be filled with the color it is pointer into the fractal.
- You can go out of the Pipet Mode: Press
 or choose in the menu:Mode | Pipet.
You can still use the content of the pipet.
or choose in the menu:Mode | Pipet.
You can still use the content of the pipet.
Using the content of the Pipet
When you see the following button in a Dialogbox:  , if you press the button, the color of the pipet is used.
, if you press the button, the color of the pipet is used.
Common Color Settings
Cursor Color
Background Color
The Background Color is used when drawing the fractal Window and exporting to a bmp-file, while using transparency.
- Press
 or choose in the menu:Fractal | Fractal Properties....
or choose in the menu:Fractal | Fractal Properties....
- In the new dialogbox select tab Misc.
- At Background choose the Color out from the Color Listbox, or use the Color from the pipet by pressing the Pipet button
 .
.
- Press button [OK].
Setting the Background color has only effect if the fractals has tranparant parts.
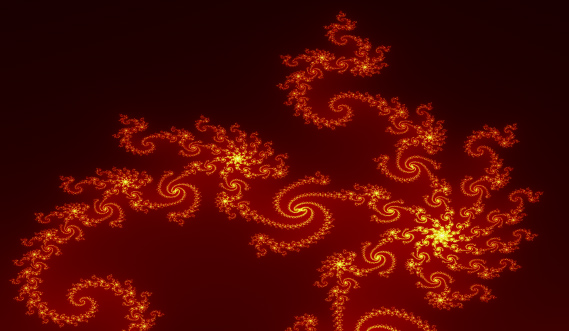
The outside of the fractal is more transparant than de yellow inside.
When choosing black as background color, the outside becomes black.
|
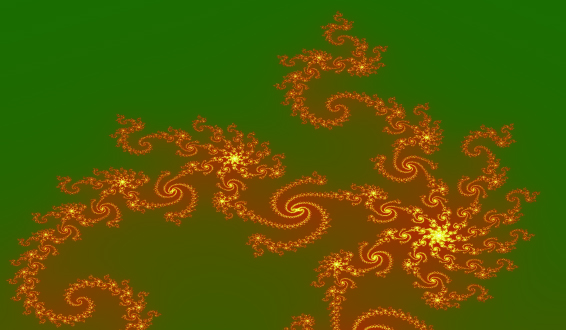
When choosing green as background color, the outside becomes green.
|
Using the Color palette
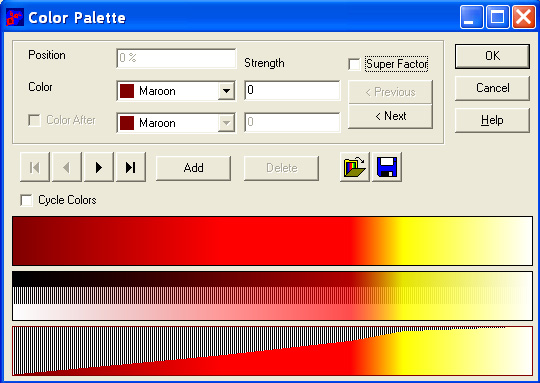
When a Properties Fractal Dialogbox is open, you can edit the color palette by pressing button Edit Palette... and the Color Palette Dialogbox appears.
A color palette has always a color at the start (most left position) and a color at the end (most right position).
You can add, move, change and delete other color positions. You can see the effect on the three colored reactangles in the Color Palette Dialogbox.
You also can load and save color palettes in files with extension ".cp1".
Browsing, adding and deleting Color Positions
You can browse througt the color position by pressing one of the buttons  :
:
 : First Color Position
: First Color Position : Previous Color Position
: Previous Color Position : Next Color Position
: Next Color Position : Last Color Position
: Last Color Position
You can delete the currently selected Color Position by pressing button
Delete,
you cannot delete the first and last Color Position.
You can add a new Color Position by pressing button
Add,
the Position of the new Color Position will be exactly in between the currently selected Position and the Next Position.
properties of a Color Position
Some propeties of the specical first and last Color Positions, are not possible to edit.
Horizontal Position
The (horizontal) position is specified in field Position. You can horizontal move it,
by changing the value, it must greater than 0 (0%) and smaller than 1 (100%).
Colors and Jump Colors
You can specify the Color for the Color Position by choosing the color at Color.
At the Color Position, you can jump from one Color to Another Color, by specifying a second Color:
Check the checkbox Color After, and choose the second color at Color After.
In the following color palette, a Color Position is selected which has a jump from dark green to grey/brown:
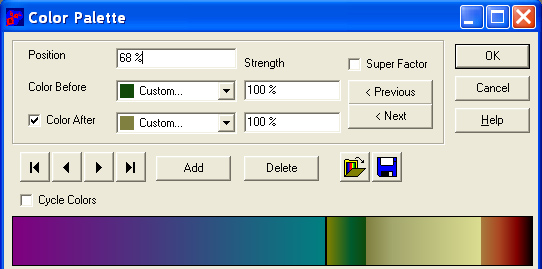
This color palette has more jumps.
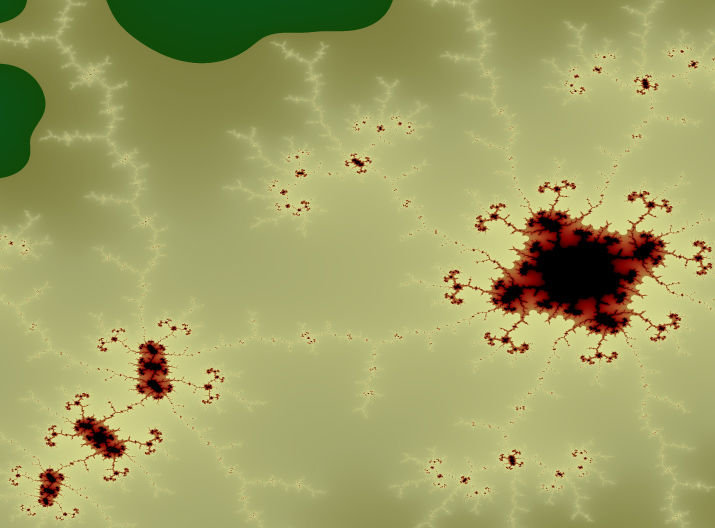
A jump between two colors becomes visible as a hard border in a fractal:
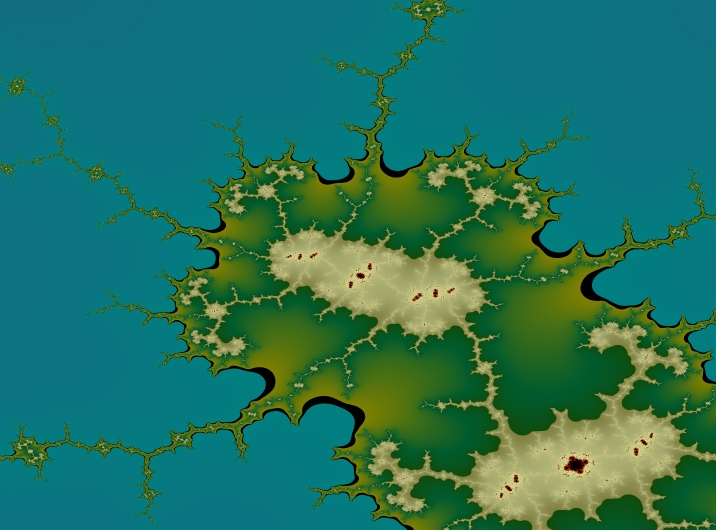
And zoomed in:
Transparant Colors
You can make a color transparant by specify a value smaller than 100 % at the fields below Strength. 0% is complete transparancy, having no Color.
in the second rectangle, you see the color transparant, and the third rectange you see how transparant the colors are.
You can Copy the Color of the Next Color Position to the current Color Positon, by pressing button > Next.
You can Copy the Color of the Previous Color Position to the current Color Positon, by pressing button < Previous.
Super Colors
Sometimes you can use Super Colors. It has only sense when map Multiple Fractal Scan pixels onto one Display Pixel.
When mixing the colors of scanned pixels to one color for the Displayed pixel,
you can highlight some colors by extrapolation to darker than black and lighter than white, redder than red etc.
With this technique you can search for centain fractal values bij giving them a "super color".
When the Color Palette can use Super Colors, a checkbox Super Factor is visible.
When checking this checkbox, you can access these properties in the dialogbox.
A Super color has two extra properties: a Super Factor and a Reference Color. When using the color before mixing,
the difference between the Color and the Reference Color is made bigger with a factor specified by Super Factor.
So you get a more twinkling and glittering effect.
For example, when using Color yellow and Reference Color black with Super Factor 3, when mixing the yellow color is three times lighter (gives three times more light).
Another example, when the Reference Color is white, this super color strongly decrease blue when mixing, because the difference between yellow and white, is that yellow has less or no light from blue.
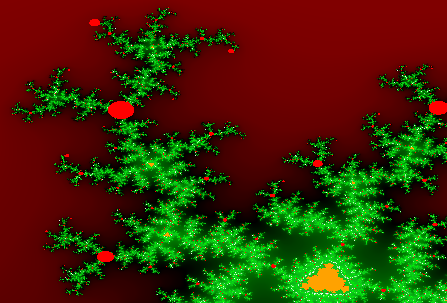
No Super Colors.
For every displayed pixel, one scanned pixel.
|
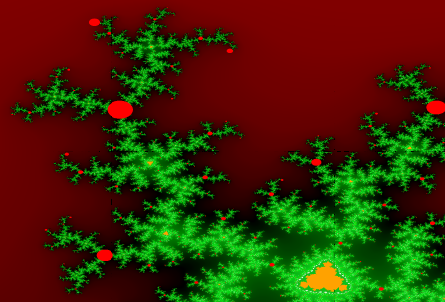
No Super Colors.
For every displayed pixel, a square of 3 times 3 scanned pixels.
|
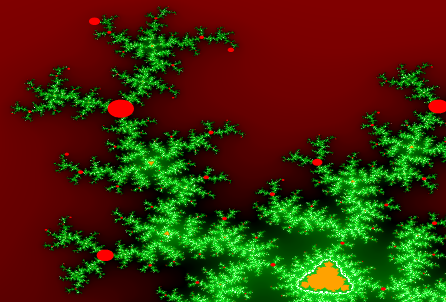
White has a Super Factor 3 and a reference color black.
For every displayed pixel, a square of 3 times 3 scanned pixels.
|

White has a Super Factor 7 and a reference color black.
For every displayed pixel, a square of 3 times 3 scanned pixels.
|
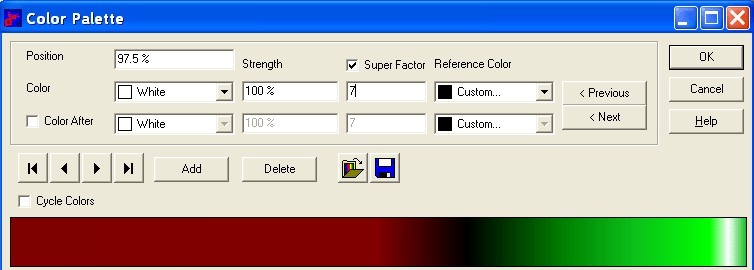
Here is a Color Palette Dialogbox with the white color selected, as a Super Color:
loading and saving to files
You can save the Color Palette to a file:
- Press
 .
.
- Type or choose a file.
- Press button [OK].
You can load a Color Palette from a file:
- Press
 .
.
- Type or choose a file.
- Press button [OK].
 or choose in the menu:Mode | Pipet.
The Cursor will change into a pipet.
or choose in the menu:Mode | Pipet.
The Cursor will change into a pipet. or choose in the menu:Mode | Pipet.
You can still use the content of the pipet.
or choose in the menu:Mode | Pipet.
You can still use the content of the pipet. , if you press the button, the color of the pipet is used.
, if you press the button, the color of the pipet is used. or choose in the menu:Fractal | Fractal Properties....
or choose in the menu:Fractal | Fractal Properties.... or choose in the menu:Mode | Zoom in.
or choose in the menu:Mode | Zoom in.


 :
:
 : First Color Position
: First Color Position : Previous Color Position
: Previous Color Position : Next Color Position
: Next Color Position : Last Color Position
: Last Color Position







 .
. .
.